There are so many people taking the Cisco 300-410 exam because this is a very popular exam!

To take the Cisco 300-410 exam first, you need to be prepared:
- Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) Mastery of examination knowledge
- Preparation before the exam
- Pay the exam fee
- Schedule an exam
- After passing the exam
These are the most basic procedures, and you better know, this will save you a lot of trouble.
Next we answer one by one:
Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI) exam contains the following knowledge points:
- Layer 3
- VPN services
- Infrastructure security
- Infrastructure services
- Infrastructure automation
Exam preparation:
I have a few preparation methods here:
- Study hard, you can get free exam content and exam practice questions through (Facebook, Twitter, Reddit, Quora, VCECERT)
- Participate in official Microsoft training: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/training-events/training-certifications/training/training-services/courses/implementing-cisco-enterprise-advanced-routing-and-services-enarsi.html. Of course, you can also search for more online training tutorials in Google.
- Get the latest updates and a valid Cisco 300-410 dumps (https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html).
Pay: (Cisco written exams,Expert lab/practical exams)
Cisco written exams:
Use your credit card in the Pearson VUE registration system Prepay for your exam before you schedule it by purchasing an exam voucher using your Cisco Learning Credits
Expert lab/practical exams:
Expert lab/practical exam payment, cost, and registration information are found on our Book your Expert Lab/Practical Exam resource page.
PS: Exam vouchers – Learning Credits
Cisco customers and learning partners can redeem their Cisco Learning Credits for certification exam vouchers.
Schedule an exam:
The exam can usually be scheduled up to six weeks in advance, and the exam can be scheduled on the same day at the latest. For exams other than the CCIE laboratory exam, please schedule the exam at Pearson VUE. For the CCIE Lab exam, please visit the CCIE website
Success:
Within 24 hours of passing the certification exam, you will receive an email telling you the next steps. You must complete the steps that trigger the fulfillment process.
Exam and certification status recorded in the Cisco Certification Tracking System. Update your contact information in time to receive notifications about your certification. After you are certified, you will be authorized to use the Cisco certification mark that identifies you. Before using the logo, you must read and confirm the Cisco Certification Logo Agreement. You can download the logo through the certification tracking system
Above I have answered the Cisco exam process and methods, and then I will share some free Cisco 300-410 exam practice questions to help you understand your own strength.
Cisco 300-410 exam practice questions (Free test 13Q&A)
The answer is announced at the end of the article
QUESTION 1
An engineer configured two routers connected to two different service providers using BGP with default attributes. One of the links is presenting high delay, which causes slowness in the network. Which BGP attribute must the engineer configure to avoid using the high-delay ISP link if the second ISP link is up?
A. LOCAL_PREF
B. MED
C. WEIGHT
D. AS-PATH
QUESTION 2
Refer to the exhibit. Users report that IP addresses cannot be acquired from the DHCP server. The DHCP server is
configured as shown. About 300 total nonconcurrent users are using this DHCP server, but none of them are active for
more than two hours per day. Which action fixes the issue within the current resources?
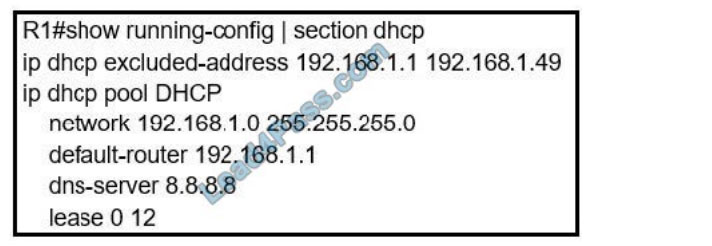
A. Modify the subnet mask to the network 192.168.1.0 255.255.254.0 command in the DHCP pool
B. Configure the DHCP lease time to a smaller value
C. Configure the DHCP lease time to a bigger value
D. Add the network 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 command to the DHCP pool
QUESTION 3
Refer to the exhibit.

An engineer is troubleshooting BGP on a device but discovers that the clock on the device does not correspond to the
time stamp of the log entries. Which action ensures consistency between the two times?
A. Configure the service timestamps log uptime command in global configuration mode.
B. Configure the logging clock synchronize command in global configuration mode.
C. Configure the service timestamps log datetime localtime command in global configuration mode.
D. Make sure that the clock on the device is synchronized with an NTP server.
The Time zone needs to be changed. default it UTC Central European Time (CET)
https://community.cisco.com/t5/networking-documents/router-log-timestamp-entries-are-different-from-the-systemclock/ta-p/3132258
QUESTION 4
A DMVPN single hub topology is using IPsec + mGRE with OSPF. What should be configured on the hub to ensure it
will be the designated router?
A. tunnel interface of the hub with ip nhrp ospf dr
B. OSPF priority to 0
C. route map to set the metrics of learned routes to 110
D. OSPF priority greater than 1
By default, the priority is 1 on all routers so we can set the OSPF priority of the hub to a value which is greater than 1 to
make sure it would become the DR.
QUESTION 5
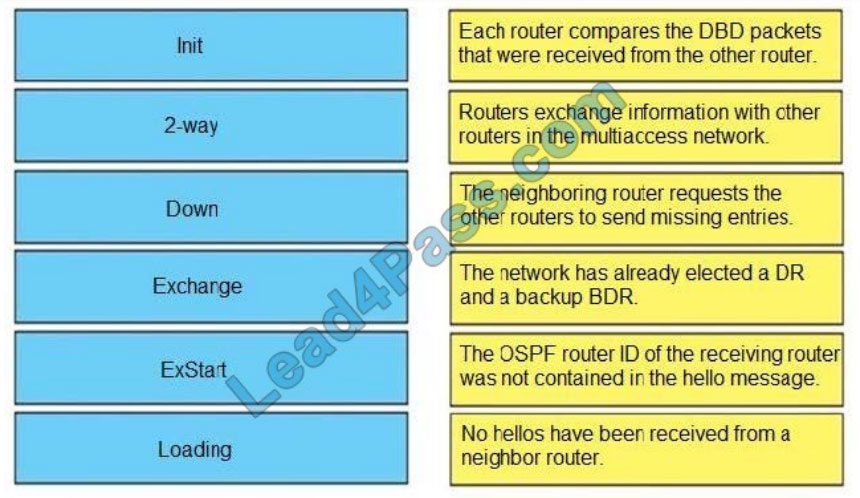
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the OSPF adjacency states from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:
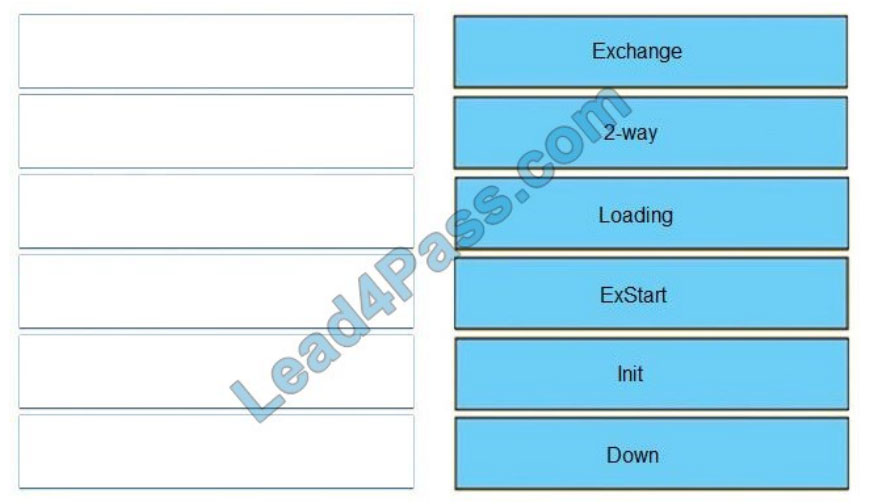

Down
This is the first OSPF neighbor state. It means that no information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor, but
hello packets can still be sent to the neighbor in this state. During the fully adjacent neighbor state, if a router doesn\\’t receive
hello packet from a neighbor within the Router Dead Interval time (RouterDeadInterval = 4*HelloInterval by default) or if the manually configured neighbor is being removed from the configuration, then the neighbor state changes from Full to Down.
Attempt
This state is only valid for manually configured neighbors in an NBMA environment. In Attempt state, the router sends
unicast hello packets every poll interval to the neighbor, from which hellos have not been received within the dead
interval.
Init
This state specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving router\\’s ID was not
included in the hello packet. When a router receives a hello packet from a neighbor, it should list the sender\\’s router ID in its hello packet as an acknowledgment that it received a valid hello packet.
2-Way
This state designates that bi-directional communication has been established between two routers. Bi-directional means that each router has seen the other\\’s hello packet. This state is attained when the router receiving the hello packet sees its own Router ID within the received hello packet\\’s neighbor field. At this state, a router decides whether to become adjacent with this neighbor. On broadcast media and non-broadcast multiaccess networks, a router becomes full only with the designated router (DR) and the backup designated router (BDR); it stays in the 2-way state with all other neighbors.
On Point-to-point and Point-to-multipoint networks, a router becomes full with all connected routers.
At the end of this stage, the DR and BDR for broadcast and non-broadcast multiacess networks are elected. For more
information on the DR election process, refer to DR Election. Note: Receiving a Database Descriptor (DBD) packet from
a neighbor in the init state will also a cause a transition to 2-way state.
Exstart
Once the DR and BDR are elected, the actual process of exchanging link state information can start between the
routers and their DR and BDR. (ie. Shared or NBMA networks). In this state, the routers and their DR and BDR
establish a master-slave relationship and choose the initial sequence number for adjacency formation. The router with the higher router ID becomes the master and starts the exchange, and as such, is the only router that can increment the sequence number. Note that one would logically conclude that the DR/BDR with the highest router ID will become the master during this process of master-slave relation. Remember that the DR/BDR election might be purely by virtue of a higher priority configured on the router instead of highest router ID. Thus, it is possible that a DR plays the role of slave. And also note that master/slave election is on a per-neighbor basis.
Exchange
In the exchange state, OSPF routers exchange database descriptor (DBD) packets. Database descriptors contain linkstate advertisement (LSA) headers only and describe the contents of the entire link-state database. Each DBD packet has a sequence number which can be incremented only by master which is explicitly acknowledged by slave. Routers also send link-state request packets and link-state update packets (which contain the entire LSA) in this state. The contents of the DBD received are compared to the information contained in the routers link-state database to check if new or more current link-state information is available with the neighbor.
Loading
In this state, the actual exchange of link state information occurs. Based on the information provided by the DBDs,
routers send link-state request packets. The neighbor then provides the requested link- state information in link-state
update packets. During the adjacency, if a router receives an outdated or missing LSA, it requests that LSA by sending a linkstate request packet. All link-state update packets are acknowledged.
Full
In this state, routers are fully adjacent with each other. All the router and network LSAs are exchanged and the routers\\’ databases are fully synchronized. Full is the normal state for an OSPF router. If a router is stuck in another state, it is an indication that there are problems in forming adjacencies. The only exception to this is the 2-way state, which is normal in a broadcast network. Routers achieve the FULL state with their DR and BDR in NBMA/broadcast media and FULL state with every neighbor in the remaining media such as point-to- point and point-to-multipoint.
Note: The DR and BDR that achieve FULL state with every router on the segment will display FULL/DROTHER when
you enter the show ip ospf neighbor command on either a DR or BDR. This simply means that the neighbor is not a DR
or BDR, but since the router on which the command was entered is either a DR or BDR, this shows the neighbor as
FULL/DROTHER.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
+
Each router compares the DBD packets that were received from the other router: Exchange
+
Routers exchange information with other routers in the multiaccess network: Exstart
+
The neighboring router requests the other routers to send missing entries: Loading
+
The network has already elected a DR and a backup BDR: 2-way
+
The OSPF router ID of the receiving router was not contained in the hello message: Init
+
No hellos have been received from a neighbor router: Down
When OSPF adjacency is formed, a router goes through several state changes before it becomes fully adjacent with its
neighbor.
The states are Down -> Attempt (optional) -> Init -> 2-Way -> Exstart -> Exchange -> Loading -> Full. Short descriptions about these states are listed below:
Down: no information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor. Attempt: only valid for manually configured
neighbors in an NBMA environment. In Attempt state, the router sends unicast hello packets every poll interval to the
neighbor, from which hellos have not been received within the dead interval.
Init: specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving router\\’s ID was not
included in the hello packet
2-Way: indicates bi-directional communication has been established between two routers. Exstart: Once the DR and
BDR are elected, the actual process of exchanging link state information can start between the routers and their DR
and BDR.
Exchange: OSPF routers exchange and compare database descriptor (DBD) packets Loading: In this state, the actual
exchange of link state information occurs. Outdated or missing entries are also requested to be resent.
Full: routers are fully adjacent with each other
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f0e.shtml
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
QUESTION 6
What is the output of the following command: show ip vrf
A. Show\\’s default RD values
B. Displays IP routing table information associated with a VRF
C. Show\\’s routing protocol information associated with a VRF.
D. Displays the ARP table (static and dynamic entries) in the specified VRF
QUESTION 7
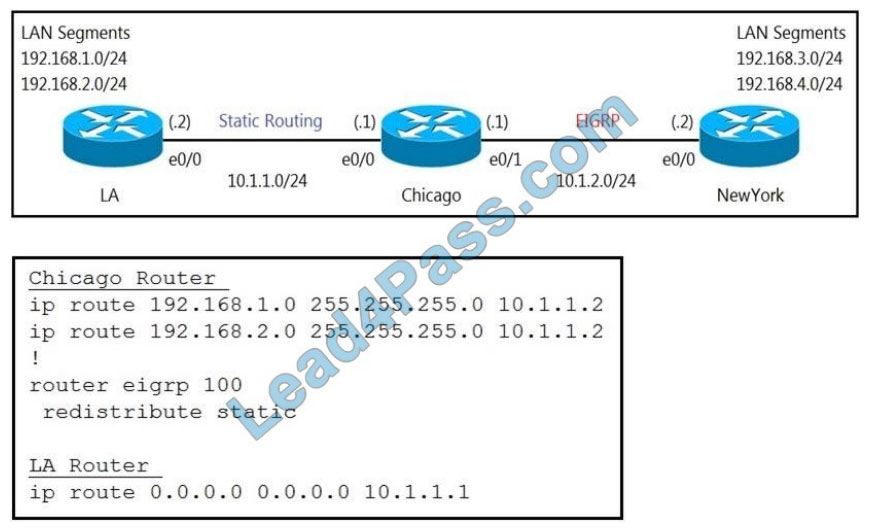
Refer to the exhibits. A user on the 192.168.1.0/24 network can successfully ping 192.168.3.1, but the administrator
cannot ping 192.168.3.1 from the LA router. Which set of configurations fixes the issue?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
QUESTION 8

Refer to the exhibit.Which routes from OSPF process 5 are redistributed into EIGRP?
A. E1 and E2 subnets matching access list TO-OSPF
B. E1 and E2 subnets matching prefix list TO-OSPF
C. only E2 subnets matching access list TO-OSPF
D. only E1 subnets matching prefix listTO-OS1
QUESTION 9
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the packet types from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place:
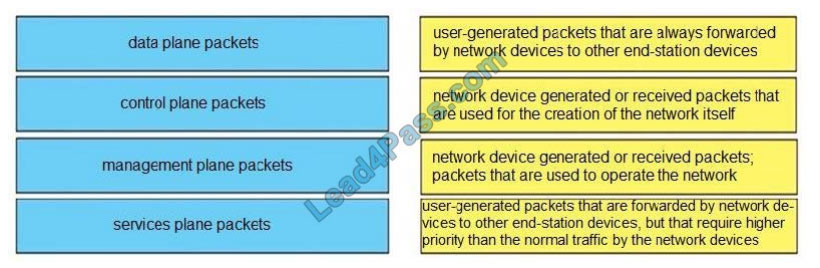
Correct Answer:
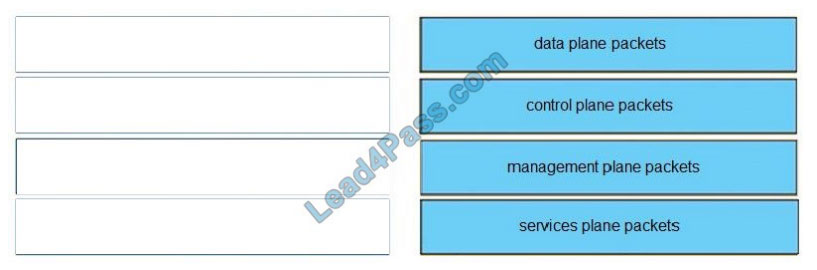
Unlike legacy network technologies such as ISDN, Frame Relay, and ATM that defined separate data and control
channels, IP carries all packets within a single pipe. Thus, IP network devices such as routers and switches must be
able to distinguish between data plane, control plane, and management plane packets to treat each packet
appropriately. From an IP traffic plane perspective, packets may be divided into four distinct, logical groups:
1.
Data plane packets -End-station, user-generated packets that are always forwarded by network devices to other endstation devices. From the perspective of the network device, data plane packets always have a transit destination IP
address and can be handled by normal, destination IP address- based forwarding processes.
2.
Control plane packets -Network device generated or received packets that are used for the creation and operation of
the network itself. From the perspective of the network device, control plane packets always have a receive destination
IP address and are handled by the CPU in the network device route processor. Examples include protocols such as
ARP, BGP, OSPF, and other protocols that glue the network together.
3.
Management plane packets -Network device generated or received packets, or management station generated or
received packets that are used to manage the network. From the perspective of the network device, management plane
packets always have a receive destination IP address and are handled by the CPU in the network device route
processor. Examples include protocols such as Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH), TFTP, SNMP, FTP, NTP, and other
protocols used to manage the device and/or network.
4.
Services plane packets -A special case of data plane packets, services plane packets are also user- generated packets
that are also forwarded by network devices to other end-station devices, but that require high-touch handling by the
network device (above and beyond normal, destination IP address-based forwarding) to forward the packet.
Examples of high-touch handling include such functions as GRE encapsulation, QoS, MPLS VPNs, and SSL/IPsec
encryption/decryption, etc. From the perspective of the network device, services plane packets may have a transit
destination IP address, or may have a receive destination IP address (for example, in the case of a VPN tunnel
endpoint).
Reference: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/resources/copp_best_practices
QUESTION 10
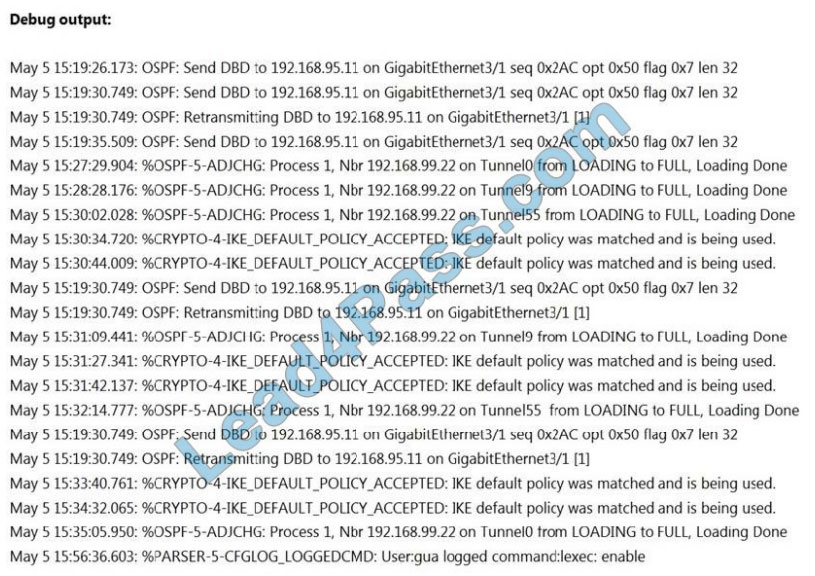
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting OSPF adjacency issue by going through the console
logs in the router, but due to an overwhelming log messages stream, it is impossible to capture the problem. Which two commands reduce console log messages to relevant OSPF neighbor problem details so that the issue can be resolved? (Choose two.)
A. debug condition ospf neighbor
B. debug condition interface
C. debug condition session-id ADJCHG
D. debug condition all
QUESTION 11
Refer to the exhibit. What does the imp-null tag represent in the MPLS VPN cloud?

A. Pop the label
B. Impose the label
C. Include the EXP bit
D. Exclude the EXP bit
The imp-null (implicit null) tag instructs the upstream router to pop the tag entry off the tag stack before forwarding the packet. Note: pop means remove the top MPLS label
QUESTION 12
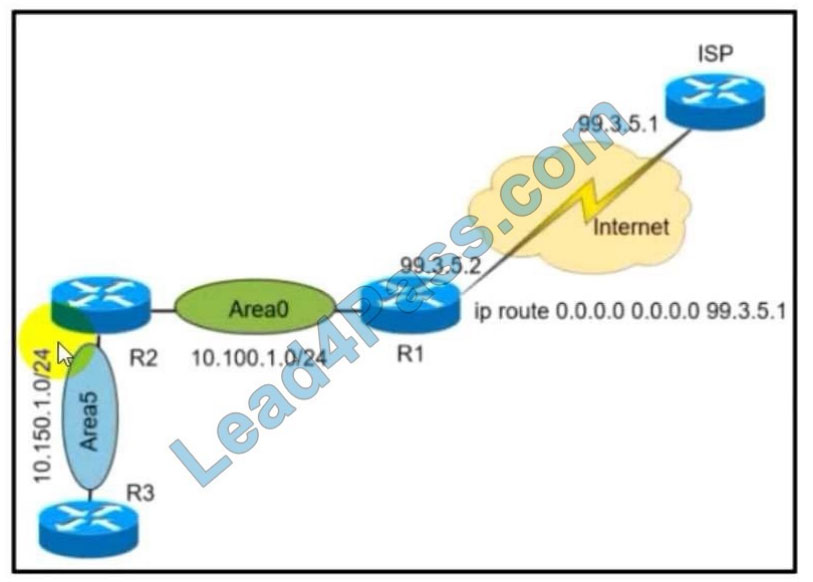
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator redistributed the default static route into OSPF toward all internal routers to reach to Internet. Which set of commands restores reachability to the Internet by internal routers?
A. router ospf 1 default-information originate
B. router ospf 1 network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
C. router ospf 1 redistribute connected 0.0.0.0
D. router ospf 1 redistribute static subnets
QUESTION 13
Which configuration adds an IPv4 interface to an OSPFv3 process in OSPFv3 address family configuration?
A. router ospfv3 1 address-family ipv4
B. Router(config-router)#ospfv3 1 ipv4 area 0
C. Router(config-if)#ospfv3 1 ipv4 area 0
D. router ospfv3 1 address-family ipv4 unicast
Verify answer:
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Q12 | Q13 |
| A | B | C | D | image | A | D | A | image | AB | A | A | D |
The complete Cisco 300-410 exam dump has Total Questions: 254 Q&A, please visit https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html
Cisco 300-410 exam PDF, 13Q&A free download
Google Drive:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1p_-zonhRS3vSDDeW7LNxOpn27anTPAS7/view?usp=sharing
More related exam practice questions and exam dumps: https://www.vcecert.com/cisco-dumps/
Thank you for reading! I prepared a lot of content very carefully. To sum up, I have shared the Cisco 300-410 exam practice questions, exam dumps, exam PDF, exam questions, and answers.
If you like, you can bookmark and share!